Making Sense of Sensors Part 2- Type B
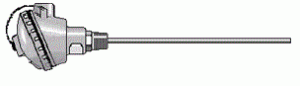
Thermocouple Type B: Platinum – 30% Rhodium (+) vs. Platinum – 6% Rhodium (-) With a general application range from 870 – 1700°C (1600 –
Call us

Thermocouple Type B: Platinum – 30% Rhodium (+) vs. Platinum – 6% Rhodium (-) With a general application range from 870 – 1700°C (1600 –
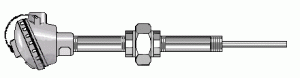
Thermocouple Type C: Type C (Tungsten 5% Rhenium – Tungsten 26% Rhenium) thermocouples are suited for measurements in the 0 – 2320°C (32 – 4200°F) range.
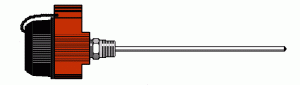
Thermocouple Type E: Type E (Chromel®/Constantan) thermocouple is composed of a positive leg of Chromel® (nickel/10% chromium) and a negative leg of Constantan (nickel/45% copper). The
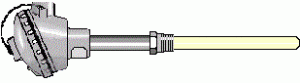
Thermocouple Type J: Type J (Iron–Constantan) is a common general purpose sensor as it is one of the most linear thermocouples. Type J thermocouples have an
Thermocouple Type K: Type K (Chromel®–Alumel®) is the most common general-purpose thermocouple. It is inexpensive, and a wide variety of probes are available in its −200 °C
Thermocouple Type N: Type N (Nicrosil/Nisil) thermocouple has a Nicrosil (nickel-14%, chromium-1.5%, and silicon) positive leg, and a Nisil (nickel- 4.5%, silicon-1%, and magnesium) negative leg.

Thermocouple Type R: Types R thermocouples, (Platinum vs. 13% Rhodium/Platinum), are usable up to 1480°C (2,700°F). They are extremely stable but reducing atmospheres are particularly damaging.

Thermocouple Type S: Platinum/10% Rhodium positive leg, and a pure platinum negative leg. The temperature range for Type S is 0 – 1450°C (32 –

Thermocouple Type T: Type T (Copper-Constantan) thermocouples are suited for measurements in the −200 to 350°C (-330 to 660°F) range. They are often used as a

The table below shows a summary of the Sense of Sensors 10 Part guide on the different types of Thermocouples. For assistance in choosing the
Copyright © 2022 Created by Pepper Digital
Disclaimer – Images for illustrative purposes only and may not be representative of the actual resolution of the camera shown.